What is a CT Scan? A Complete Beginner’s Guide
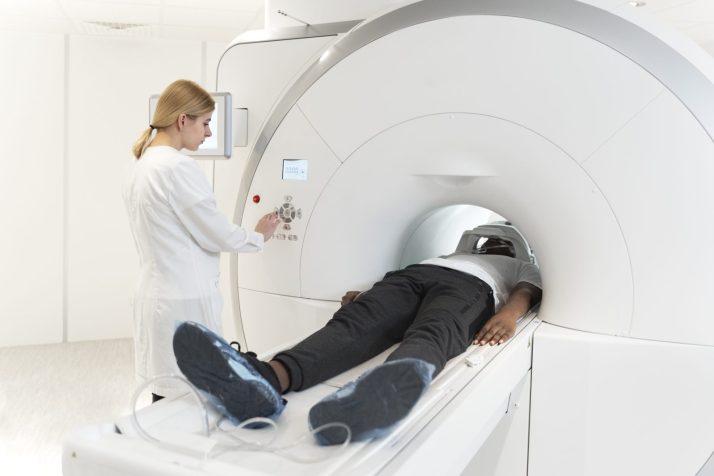
A CT scan is a vital and commonplace imaging tool. First developed in the late 1960s, computed tomography (CT scan) technology has continued to advance and improve over the decades. In the US, it is estimated that over 80 million CT scans are implemented each year, used across a wide variety of medical specialties.
This article will provide details on what CT scans are, how they work, and what to expect as a patient during the process of a CT scan.
What is a CT Scan?
A CT scan uses multiple X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body. Unlike a standard X-ray machine, a CT scanner is an X-ray tube that rotates around you while you remain still on a table. Detectors opposite the X-ray tube detect how much of the X-ray beam passes through the body.
Using computer technology, these 2D-images are compiled into 3-D images that can show cross-sectional views of the human body. The radiologist can view these images as “slices” of the body, allowing a detailed spatial view to exist of a body part or organ. CT scans are the premier tool in diagnosing injuries, diseases, or abnormalities of areas such as the head, chest, abdomen, and pelvis.
The Patient Experience: What Happens During a CT Scan?
There are several steps involved for preparing for the scan, engaging in the scan, and post-recovery.
-Preparation: If your abdomen or a GI organ like the stomach or intestines are being scanned, you might be asked to fast for a period of time before that scan. When you arrive at the hospital you will likely change into a hospital gown and remove any jewelry items that could interfere with the scanning process.
Depending upon the body part being scanned, you may be given a contrast. This is a dye that will help select parts of the body to show up better during the scan. Contrast can be ingested as a drink, injected as a shot, or given as an enema. When you receive the contrast, you may experience side effects such as a warming sensation, a metallic taste in your mouth, or feeling the need to urinate.
-The Scan: You will lay down on a table that slides into the CT scanner. You will usually lie on your back but depending upon the body part or organ being scanned, the radiologist may use pillows or straps to help position your body in the best position.
It is important to remain still and relaxed during the scan. If your body moves during the procedure, the process may need to be re-done, making the scanning procedure longer.
While the scanner is working, you may hear whirring, clicking or pulsating noises. The radiologic technician is in a neighboring control room and will be in communication with you through an intercom. During the scan, the radiologist may give you instructions to either move a body part or hold your breath for a brief period to aid the imaging process. The scanning process itself causes no sensation; X-rays passing through your body are unfelt. Although the procedure does use radiation, it is of a very low dose and should not be of any health concern.
-Post-Procedure: There is no recovery period. Most patients can resume their regular activities without delay. If you received contrast, you may be encouraged to drink more fluids to help flush the contrast out of your body. This may increase your need to urinate more frequently during the rest of the day.
Common Uses of a CT Scan
CT scans are a powerful diagnostic screening tool for many of these medical concerns including:
-Cancer: In particular, organ cancers such as lung, liver, pancreas and kidney.
-Cardiovascular disease: Conditions such as coronary artery disease, blockages, and aneurysms.
-Bone Fractures
-Kidney Stones
-Infections: CT scans can detect abscesses, sinusitis, and pneumonia.
-Internal Bleeding
-Brain Injuries/Conditions: Concussions, strokes and tumors.
-Spinal Cord Injuries
CT scans are also a key instrument in monitoring medical treatment such as:
-Tumors: CT scans can measure the growth and location of tumors before, during, and after treatment.
-Metastasis: CT scans can identify if cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
-Chronic Conditions: Ailments like emphysema and kidney disease can be monitored over time to determine effectiveness of ongoing treatment.
-Infections: CT technology can the measure the effectiveness of antibiotic treatments.
-Healing Process: CT scans can check the progress of fractures or internal injuries due to trauma or surgery.
-Organ Transplants: CT scans can monitor the health of transplanted organs, determining any signs of organ rejection.
CT technology is an important tool in medical planning and observation. Instances such as:
-Surgical/Invasive Procedures (Real Time): CT scans can guide procedures , such as biopsies, drains, and nerve blocks. CT technology can assist surgeons during laparoscopic surgery , allowing much smaller incisions to occur and less tissue damage. CT scans also aid endovascular surgeons, allowing catheters and other surgical instruments to be guided through blood vessels during procedures such as stents and angioplasty.
-Complex Surgical Planning: CT scans provide the surgical team with advanced knowledge of a specific patient’s anatomy, helping them plan and choose the best surgical approach as well as anticipate potential issues. Spinal surgery is a perfect example of complex surgery that relies on CT scans; visualizing the vertebrae, discs and nerves to help plan the use of implants or instrument use.
RadiologyAssist: Your Partner in Radiologic Screening
We are the national leader in providing affordable radiologic screenings to uninsured and self-pay patients. We partner with over 1000+ high-quality accredited centers nationwide, ensuring quality and convenient care with up-front transparent pricing. Our scheduling capabilities allow our patients to get their CT scans quickly, avoiding delays in diagnosis and care.
Final Thoughts
CT scans have been used successfully as a leading diagnostic tool for nearly 50+ years. They are a safe, effective, and comfortable procedure in diagnosing numerous medical conditions , illnesses and injuries. At RadiologyAssist, we put CT scans and other radiologic screenings within affordable reach of all who need them.
Blog & Healthcare News